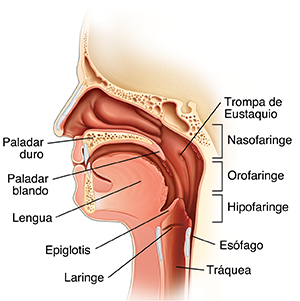
Paladar duro. Separa la nariz de la boca.
Paladar blando. La parte posterior de la parte de arriba de la boca.
Epiglotis. Mantiene la comida y los líquidos fuera de la tráquea al tragar.
Laringe (caja de voz). Esta genera el sonido que se usa para hablar.
Trompa de E ustaquio El tubo que conecta la garganta con el oído.
Nasofaringe. El área que se encuentra en la parte superior de la garganta detrás de la nariz.
Orofaringe. El área que se encuentra en la mitad de la garganta detrás de la boca.
Hipofaringe. El área que se encuentra en la parte inferior de la garganta.
Esófago. El tubo que transporta los alimentos y los líquidos desde la garganta hasta el estómago.
Tráquea. El tubo que transporta aire entre la garganta y los pulmones.
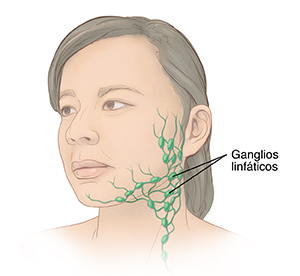
Ganglios linfáticos. Órganos con forma de frijoles que ayudan a que el cuerpo pueda luchar contra las infecciones.