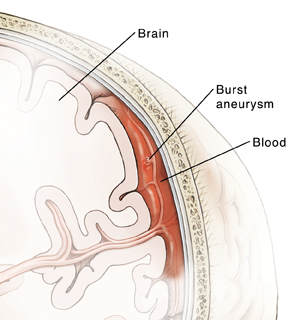
When an aneurysm bleeds, the bleeding often stops quickly on its own. But if the blood touches brain cells, the cells may be damaged. Blood in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) increases pressure on the brain, which can damage brain tissue. Leaked blood may also touch nearby arteries. This may cause these arteries to spasm and narrow, which decreases oxygen flow to the brain. This can cause further damage to the brain.
Damage to brain cells
Blood from an aneurysm can leak into the CSF in the space around the brain. The pool of blood forms a clot. Blood can irritate, damage, or destroy nearby brain cells. This may cause problems with body functions or mental skills.
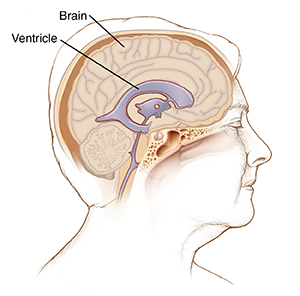
Brain fluid buildup
Blood from a torn aneurysm can block CSF circulation. This can lead to fluid buildup and increased pressure on the brain. The open spaces in the brain (ventricles) then enlarge. This problem is called hydrocephalus. It can make a person lethargic and confused. To remove leaked blood and trapped CSF, a drain may be placed in the ventricles.
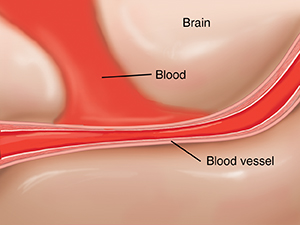
Narrowing arteries
An artery may clamp down if leaked blood touches it. This response, called vasospasm, may happen up to 14 days after an aneurysm bleeds. Vasospasm can decrease blood needed in other parts of the brain. It can be fatal. To treat vasospasm, the person's blood pressure and fluid intake are increased. Drugs such as calcium channel blockers can be given in your veins or arteries. This increases the force of the blood and widens the artery.
Your loved one’s healthcare team will answer any questions you have. After special tests are done and the cause is known, specialists are called. Treatment will begin right away if the aneurysm has already bled. The person may be too ill to know what’s going on. You may need to decide on the extent of their treatment. Choose a few family members to talk to the healthcare team. These family members can share what they learn with others. Doing this will make it simpler to keep everyone informed. Sometimes, the aneurysm leads to devastating brain injury that results in such severe injury that life support is required. Sometimes, even the most intensive treatment is not effective in saving someone's life.