A pineal cyst is a type of brain cyst. A brain cyst is an abnormal fluid-filled sac in the brain. A cyst in the brain may contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF normally bathes and cushions the brain and spinal cord. Often, a brain cyst starts before birth. They are generally not cancer (benign). Benign also means that the growth doesn't spread to other parts of the body. A pineal cyst can appear in people of any age.
Understanding the pineal gland
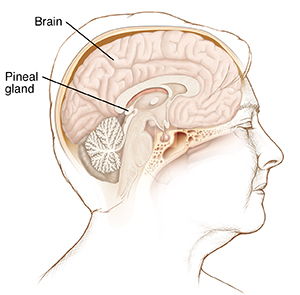
The pineal gland is a small organ in the middle of the brain. It makes melatonin. This is the hormone that regulates sleep. A pineal cyst usually only shows up on an imaging scan done for another reason. A pineal cyst seldom causes problems. If it grows large, it can affect your vision.
What causes a pineal cyst?
Researchers are not sure what causes a pineal cyst.
Symptoms of a pineal cyst
A pineal cyst does not usually cause any symptoms. In rare cases, extra CSF or bleeding into the cyst may cause headache or make it hard to look up.
In rare cases, a pineal cyst may cause CSF to build up on the brain. This is called hydrocephalus. It’s caused when the cyst blocks the flow of CSF in the brain. Hydrocephalus can cause symptoms such as:
-
Confusion
-
Vertigo
-
Double vision
-
Headaches
-
Upset stomach (nausea)
-
Sleepiness
-
Trouble walking
-
Vomiting
-
Passing out (syncope)
-
Coma
Diagnosing a pineal cyst
A pineal cyst is usually found by chance on an imaging test of the brain. This may be one of the following:
-
CT scan. This is a test that uses a series of X-rays and a computer to create images of the inside of the body.
-
MRI. This test uses large magnets and a computer to create images of the body. MRI scans of your brain may be done to get more information about the cyst and nearby tissues.
Treatment for a pineal cyst
A pineal cyst is usually only treated if it causes symptoms. If symptoms are present, your healthcare provider may recommend these treatments:
-
Endoscopic removal. This is surgery through a small tube called an endoscope.
-
Stereotactic aspiration. This is the removal of fluid from the cyst with a needle. Imaging is used to help guide the needle.
Your healthcare provider will talk with you about which treatment works best for you.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these:
-
Confusion
-
Trouble walking
-
Sudden headache
-
Vision problems