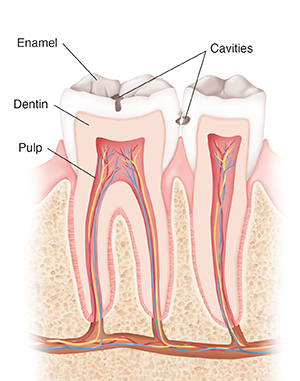
A dental cavity is a pit or crater in the surface (enamel) of a tooth. Adults and children can get cavities. A cavity exposes the sensitive inner layer of the tooth and causes pain. If the cavity isn’t treated by a dentist, it will get bigger. It may enter the pulp and cause an infection or pocket of pus (abscess) in the bone at the root end of the tooth. An infection in the tooth is a much more serious problem than a cavity. If the tooth gets infected, you'll need a root canal or the whole tooth taken out (extraction).
The pain in your tooth may be worse if you eat sweets or have hot or cold food or drinks. It may spread from the tooth to your ear or the part of your jaw on the same side.
Home care
Follow these tips when caring for yourself at home:
-
Don't have sweets or hot and cold foods and drinks. Your tooth may be sensitive to changes in temperature.
-
Put a cold pack on your jaw over the sore area to help reduce pain.
-
You may use over-the-counter medicine to ease pain, unless another medicine was prescribed. If you have long-term (chronic) liver or kidney disease, talk with your healthcare provider before using acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Also talk with your provider if you’ve had a stomach ulcer or GI (gastrointestinal) bleeding.
-
If you have signs of an infection, you will be given an antibiotic. Take it as directed.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your dentist, or as advised. Your pain may go away with the treatment given today. But only a dentist can diagnose and treat this problem to prevent further tooth damage.
Call 911
Call
-
Trouble swallowing or breathing
-
Weakness or fainting
-
Abnormal drowsiness
-
Confusion
-
Headache or stiff neck
-
Vision problems
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of the following occur:
-
Red or swollen face
-
Pain gets worse or spreads to your neck
-
Fever of 100.4 °F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider
-
Pus drains from the tooth or gum