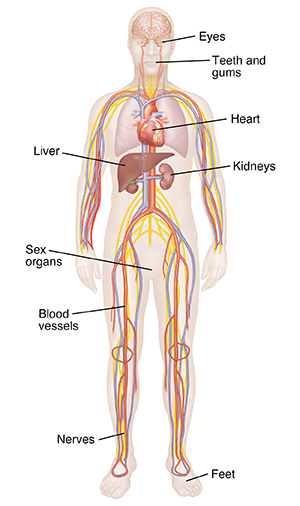
Over time, diabetes can cause complications throughout the body. They are more likely to happen if your blood sugar is often too high. They can also happen if your diabetes isn't under good control. High blood sugar can damage blood vessels in your body over time. It's important to keep your blood sugar in your target range. This can help prevent or delay complications.
Possible complications
Diabetes can cause:
-
Eye problems. These include damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, pressure in the eye, and clouding of the eye’s lens. Eye problems can lead to bleeding and blindness over time.
-
Tooth and gum problems. These can cause pain, infection, or loss of teeth and bone.
-
Blood vessel disease. This can lead to circulation problems, heart attack, or stroke. You may need a limb removed because of poor blood flow to the skin.
-
Problems with sexual function. This includes erectile dysfunction and sexual discomfort.
-
Kidney disease. This can lead to kidney failure. You may need dialysis or a kidney transplant if this happens.
-
Nerve problems. These can cause pain or loss of feeling in your feet and other parts of your body. This may lead to loss of a limb. Nerve damage may also cause hearing loss.
-
High blood pressure. This health problem puts strain on your heart and blood vessels.
-
Serious infections. These may lead to loss of toes, feet, or limbs.
-
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Having type 2 diabetes raises the risk for severe fat buildup in the liver.
-
Muscle and bone problems. These include carpal tunnel syndrome, frozen shoulder, Dupuytren contractures in the fingers, fractures, and osteoporosis.
How to prevent complications
You can help prevent these serious complications by managing your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol. This can help you feel better and stay healthy. You can help control diabetes by tracking your blood sugar levels regularly as advised by your doctor.
Eat healthy foods and exercise to prevent weight gain. Stop all tobacco products if you smoke. This will greatly improve your overall health.
Go to all of your health care appointments. Get the recommended health checks, such as blood and urine tests, blood pressure screenings, eye exams, foot checks, dental exams, and bone health tests. Also stay up-to-date on the recommended vaccines. Ask your doctor what vaccines you should have.
It's important to take medicine as directed by your doctor. Report any side effects as advised by your doctor. Also tell your doctor if you have trouble staying at healthy blood sugar levels.