ERCP stands for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. This procedure is used to view the biliary and pancreatic ducts. It's used to check diseases that affect the biliary and pancreatic ducts. It can also help find and treat any blockages.
How to say it
koh-LAN-jee-oh-pan-kree-uh-TAW-gruh-fee
How do I get ready for ERCP?
-
Talk with your healthcare provider about any health problems or allergies you have.
-
Ask your healthcare provider about the risks of ERCP. These include:
-
Pancreatitis
-
Infection
-
Bleeding
-
Tears in the bowel
-
-
You may be asked to take antibiotics ahead of time.
-
Don't take blood-thinning medicines before ERCP, as advised by your healthcare provider.
-
Don't eat or drink for 8 to 12 hours before ERCP.
-
Have someone ready to take you home.
-
Be sure your healthcare provider knows about all medicines you take. You may be told to stop taking some or all of them before the test. This includes:
-
All prescription medicines
-
Over-the-counter medicines that don’t need a prescription
-
Any illegal drugs you may use
-
Herbs, vitamins, kelp, seaweed, cough syrups, and other supplements
-
What happens during the procedure?
-
You will be given medicine through an IV (intravenous line) to help you relax.
-
Your throat is numbed.
-
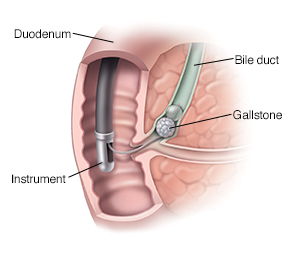
A thin tube (endoscope) is placed into your throat. It's moved down your throat through the upper digestive tract to the common bile duct opening. The endoscope lets the healthcare provider see the common bile and pancreatic ducts on a video screen.
-
A cut may be made where the common bile duct opens to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). This makes it easier to remove stones.
-
As blockages are found and taken out, X-rays are taken.
-
Contrast dye is injected through a catheter. This makes the duct show up better on the X-rays.
-
An imaging technique called fluoroscopy is done. It uses X-rays to get real-time moving images of internal organs. It's used to watch and guide progress of the ERCP.
-
In some cases, a plastic tube (stent) is placed to hold the ducts open. This stent may be replaced or taken out in 6 to 8 weeks. Or it may be left to fall out on its own. It will then pass in the stool.
After the procedure
Your healthcare provider may talk with you about the test results right away. Or you may need to schedule a return visit. Depending on your health problem and the test results, you may go home the same day. Or you may have to spend the night in the hospital. If you are sent home, follow these guidelines:
-
Unless told otherwise by your healthcare provider, you can go back to a normal routine the day after the ERCP.
-
If a cut was made in the duct, don't take blood-thinning medicines such as aspirin for 5 to 7 days, or as advised by your healthcare provider.
-
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a fever or belly pain. These may be signs of an infection or a tear in your bowel.