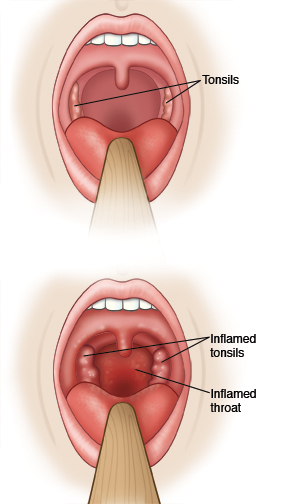
You have had a positive test for strep throat. Strep throat is a bacterial infection that can be spread to others. It's spread by coughing, kissing, sharing glasses or eating utensils, or by touching others after touching your mouth or nose. Symptoms may include:
-
Throat pain that's worse when you swallow.
-
Aching all over.
-
Headache.
-
Swollen lymph nodes at the front of the neck.
-
Red, swollen tonsils that may have white patches.
-
Fever.
It's treated with antibiotic medicine. You should start to feel better in 1 to 2 days with treatment.
Home care
-
Rest at home. Drink plenty of fluids so you won't get dehydrated.
-
You can return to school or work if you are feeling better, have been taking the antibiotic for at least 24 hours, and don't have a fever.
-
If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics. It's also important to prevent medicine-resistant germs from developing. If you were given an antibiotic shot, you don't need any more antibiotics.
-
You may use acetaminophen or ibuprofen to control pain or fever unless another medicine is prescribed for this. Talk with your doctor before taking these medicines if you have chronic liver or kidney disease or if you've had a stomach ulcer, digestive bleeding, or if you're taking blood thinners.
-
Throat lozenges or sprays help reduce pain. Gargling with warm saltwater will also ease throat pain. Dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of salt in 1 glass of warm water. This may be useful just before meals.
-
Soft foods and cool or warm fluids are best. Don't eat salty or spicy foods.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your doctor if you don't get better over the next week.
When to contact your doctor
Contact your doctor right away if:
-
You have a fever of 100.4ºF (38ºC) or higher, or as directed by your doctor.
-
You have ear pain, sinus pain, or headache that is new or gets worse.
-
You have painful lumps in the back of neck.
-
Your neck is stiff.
-
Your lymph nodes are getting larger or becoming soft in the middle.
-
You have trouble swallowing liquids or you can't open your mouth wide because of throat pain.
-
You have signs of dehydration. These include very dark urine or no urine, sunken eyes, and dizziness.
-
Your breathing is noisy.
-
You have a rash.
Call 911
Call
-
You have trouble breathing.
-
You can't swallow or talk.
-
You speak with a muffled voice.
Prevention
Here are steps you can take to help prevent an infection:
-
Wash your hands often with soap and clean, running water for at least 20 seconds.
-
Don’t have close contact with people who have sore throats, colds, or other upper respiratory infections.
-
Don’t smoke, and stay away from secondhand smoke.