Conjunctivitis is an irritation of the thin membrane covering the eye and the inside of the eyelid. This membrane is called the conjunctiva. The condition is often called pinkeye or redeye because the eye looks pink or red. The eye may also be swollen, itchy, burning, or tearing. A watery or mucous discharge may occur. This type of conjunctivitis is not contagious.
Allergic conjunctivitis is caused by an allergen. Allergens are substances that cause the body to react with certain symptoms. Allergens that cause eye irritation include things such as house dust, smoke, or pollen in the air. This can occur seasonally, most often in the spring. Other possible allergens that may cause symptoms include cosmetics, perfumes, animal saliva or dander, chlorine in swimming pools, or contact lenses.
Home care
-
Eye drops may be prescribed to reduce itching and redness. Use these as directed. Otherwise, over-the-counter lubricating eye drops, sometimes referred to as artificial tears, may be used.
-
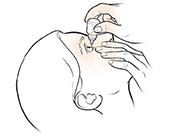
Apply a cool compress (towel soaked in cool water) to the affected eye 3 to 4 times a day. It can reduce swelling and itching.
-
It's common to have mucus drainage during the night. This causes the eyelids to become crusted by morning. Use a warm, wet cloth to wipe this away. You may also use saline irrigating solution or artificial tears to rinse away mucus in the eye. Don't patch the eye.
-
You may use acetaminophen or ibuprofen to control pain, unless another medicine was prescribed. Talk with your healthcare provider if you have chronic liver or kidney disease before using these medicines. Also talk with your provider if you have ever had a stomach ulcer or digestive bleeding.
-
Don't wear contact lenses until your eyes have healed and all symptoms are gone.
-
Avoid the allergen as much as possible, if the allergen is known.
-
Don't rub your eyes.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised. You may be referred to an allergist.
When to seek medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Increased eyelid swelling
-
New or worsening drainage from the eye
-
Increasing redness around the eye
-
Facial swelling