Your heart’s job is to pump blood through your body. That job starts with pumping blood through the heart itself. Inside your heart, blood passes through a series of one-way gates (valves). If a valve doesn't work correctly, not enough blood moves forward. A problem heart valve may not open wide enough may not close tightly enough, or both. In any case, not enough blood is sent through the heart muscle or out to the body.
Symptoms of heart valve problems
You can have a problem valve for decades yet have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may come on so slowly that you barely notice them. In other cases, symptoms may appear quickly. You might have 1 or more of these symptoms:
-
Problems breathing when you lie down, exert yourself, or get stressed emotionally
-
Pain, pressure, tightness, or numbness in your chest, neck, back, or arms (angina)
-
Feeling dizzy, faint, or lightheaded
-
Tiredness, especially with activity or as the day goes on
-
Waking up at night coughing or short of breath
-
A fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
-
A fluttering feeling in your chest
-
Swollen ankles or feet
-
Fainting, especially on standing up or with exertion
Common causes of valve problems
People of any age can have heart valve trouble. You may have been born with a problem valve. Or a valve may have worn out as you’ve aged. It may not be possible to pinpoint what caused your valve problem. But common causes include:
-
Buildup of calcium or scar tissue on a valve
-
Rheumatic fever and some other infections and diseases
-
High blood pressure
-
Other heart problems, such as coronary artery disease
-
Congenital defects of the heart valves
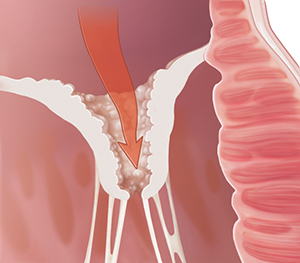
Problems opening (stenosis)
When a valve doesn’t open all the way, the problem is called stenosis. The leaflets may be stuck together or too stiff to open fully. When the valve doesn’t open fully, blood has to flow through a smaller opening. So the heart muscle has to work harder to push the blood through the valve.
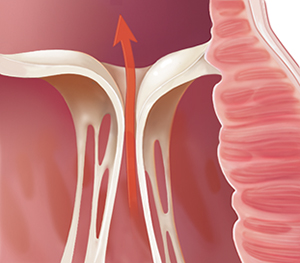
Problems closing (regurgitation)
When a valve doesn’t close tightly enough and blood leaks backward through the valve, the problem is called regurgitation or insufficiency. The valve itself may be described as leaky. Leaflets may fit together poorly. Or the structures that support them may be torn. Some blood leaks through the valve back into the chamber it just left. So the heart has to move that blood twice. This can result in heart muscle damage.