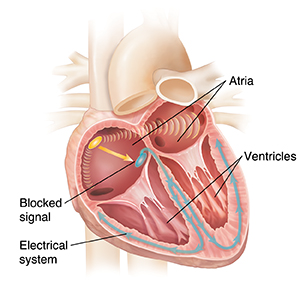
Heart block is a condition in which the electrical wiring system of the heart doesn't work correctly. It usually results in a slow heartbeat that's either regular or irregular. This condition may not cause symptoms.
With third-degree heart block, the upper chambers of the heart are beating normally, but the electrical signals are not relayed from the upper chambers of the heart (atria) to the lower chambers (ventricles). The signaling system in the lower chambers may take over as a backup. But this doesn't work well because the normal rate in the ventricles is much slower. People with third-degree heart block usually have a very slow heartbeat. Because their heart is beating so slowly, it doesn't do a good job of sending blood throughout the body. People with heart block often have symptoms.
Third-degree heart block is sometimes called complete heart block.
What causes third-degree heart block?
Third-degree heart block may be caused by:
-
Damage to the heart from surgery.
-
Damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack.
-
Other types of heart disease that result in heart muscle damage.
-
Heart valve disease.
-
Other diseases, including rheumatic fever and sarcoidosis.
-
Some medicines.
-
Older age.
Some babies are born with heart block. Heart block may also run in families.
What are the symptoms of third-degree heart block?
Symptoms of third-degree heart block may include:
-
Feeling lightheaded, faint, or dizzy.
-
Feeling tired.
-
Feeling short of breath.
How is third-degree heart block treated?
Third-degree heart block is a serious condition that needs to be treated right away. Treatments include:
-
Taking medicines to increase the heart rate for the short term.
-
Stopping medicines, if they are causing the heart block.
-
Getting a pacemaker.
What are possible complications of third-degree heart block?
Third-degree heart block may cause a sudden loss of consciousness (syncope). It may also cause the heart to suddenly stop beating (sudden cardiac arrest).
When should I call my doctor?
Contact your health care provider right away if you have:
-
Unusual tiredness.
-
Weakness or dizziness.
-
Unusual drowsiness or confusion.
-
Pain that gets worse.
-
Symptoms that don’t get better with treatment, or symptoms that get worse.
-
New symptoms.
Call 911
Call
-
Shortness of breath.
-
Chest pain.
-
Fainting.
Author: Freed, Becca
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.