Pneumonia is a serious lung infection. It can affect 1 or both lungs. Many cases of pneumonia are caused by bacteria or viruses. Fungi may also cause pneumonia. But this is less common.
You may get pneumonia after an illness, such as a cold, flu, or bronchitis. Those most at risk for pneumonia include:
-
Babies
-
Children
-
Older adults
-
Smokers
-
People with long-term (chronic) health problems or weak immune systems
Healthy lungs
-
Air travels in and out of the lungs through tubes called airways.
-
The tubes branch into smaller passages called bronchioles. These end in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
-
Blood vessels surrounding the alveoli take oxygen into the bloodstream. At the same time, the alveoli remove carbon dioxide (a waste gas) from the blood. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled.
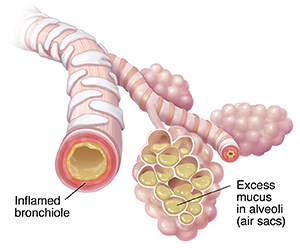
When you have pneumonia
-
Pneumonia causes the bronchioles and the alveoli to fill with excess mucus or pus. They become inflamed.
-
Your body’s response may be to cough. This can help clear out the fluid.
-
The fluid (mucus) you cough up may look green or dark yellow.
-
The excess mucus may make you feel short of breath.
-
The inflammation and infection may give you a fever.
What are the symptoms?
Pneumonia symptoms can come without warning. At first, you may think you have a cold or flu. But symptoms may get worse quickly. They then turn into pneumonia. Symptoms can be different for bacterial and viral pneumonia. They may be mild or severe. Common symptoms may include:
-
Severe cough with green or yellow mucus that doesn't get better. Or gets worse.
-
Fever and chills
-
Upset stomach (nausea), vomiting, or diarrhea
-
Loss of appetite
-
Shortness of breath with normal daily activities
-
Increased heart rate
-
Chest pain or discomfort when breathing in or coughing
-
Headache
-
A lot of sweating and clammy skin
-
Severe tiredness (fatigue)