When your Pap test is sent to the lab, the lab studies your cell samples and reports any abnormal cell changes. Your healthcare provider can discuss these changes with you. In some cases, an abnormal Pap test is due to an infection. More serious cell changes range from dysplasia to cancer. Talk with your healthcare provider about your Pap test.
Normal results
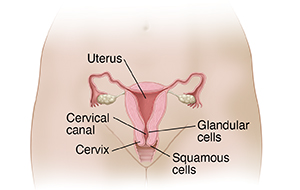
Cervical cells, even normal ones, are always changing. As they mature, normal squamous cells move from deeper layers within the cervix. Over time, these cells flatten and cover the surface of the cervix. Within the cervical canal, the cells are different. These glandular cells are taller and not as flat as the cells on the surface of the cervix. When a Pap test sample shows healthy cells of both types, the results are negative. Keep having Pap tests as often as directed.
Abnormal results
A positive Pap test result means some cells in the sample showed abnormal changes. These results are grouped by the type of cell change and the location, or extent, of the changes. Depending on the results, you may need further testing.
-
Inflammation. Noncancerous changes are present. They may be due to normal cell repair. Or they may be caused by an infection, such as HPV or yeast. Further testing may be needed. (Also called reactive cellular changes.)
-
Atypical squamous cells. Test results are unclear. Cells on the surface of the cervix show changes, but their significance is not yet known. Testing for HPV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may be needed. Treatment may be needed. (Reported as ASC-US or ASC-H.)
-
Atypical glandular cells. Cells lining the cervical canal show abnormal changes. More testing is likely. You may also have treatment to destroy or remove problem cells. (Reported as AGC.)
-
Mild dysplasia. Cells show distinct changes. More testing or HPV typing may be done. You may also have treatment to destroy or remove problem cells. (Reported as low-grade SIL or CIN 1.)
-
Moderate to severe dysplasia. Cells show precancerous changes. Or noninvasive cancer (carcinoma in situ) may be present. Treatment to destroy or remove problem cells is likely. (Reported as high-grade SIL or CIN 2 or CIN 3.)
-
Cancer. Different types of cancer may be found by your Pap test. More tests to assess the cancer's extent are likely. The type of treatment will depend on the test results and other factors, such as age and health history. (Reported as squamous cell carcinoma, endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ, or adenocarcinoma.)
Featured in