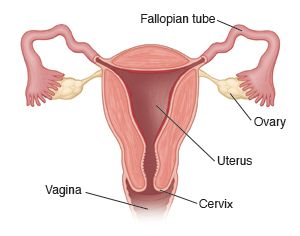
Heavy menstrual bleeding means that your periods are heavier or longer than normal. You may soak through a pad or tampon every 1 to 3 hours on the heaviest days of your period. You may also pass large, dark clots. And your periods may last longer than 7 days.
If you have heavy periods often, this can cause a problem called anemia. With anemia, your red blood cell count is too low. Red blood cells are needed as they help carry oxygen all over your body. Severe anemia may make you look pale and feel weak or tired. You might also get short of breath easily.
There are many possible causes of heavy menstrual bleeding. Hormonal imbalance is the most common cause. Having noncancer (benign) growths in your uterus is another cause. These include fibroids or polyps. Taking certain medicines or having certain health problems or bleeding disorders are also causes.
To treat heavy menstrual bleeding, your healthcare provider may prescribe medicines first. If these don’t help, you may need more testing and treatments.
Home care
Medicines
If you’re prescribed medicines, take them as directed.
-
To help control heavy bleeding, any of these may be used:
-
Hormone therapy (this includes all types of hormonal birth control such as pills, shots, cream, ring, patch, or hormone-releasing IUD)
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen
-
Antifibrinolytic medicines, such as tranexamic acid
-
-
To help treat anemia, iron supplements may be prescribed.
General care
-
Get plenty of rest if you tire easily. Avoid heavy exertion.
-
To help ease pain or cramping, try using a heating pad on the lower belly or back. A warm bath may also help.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised.
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Heavier bleeding (soaking 1 pad or tampon every hour for 3 hours)
-
Heavy bleeding that lasts longer than 1 week
-
Fever of 100.4ºF (38ºC) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Pain or cramping that gets worse instead of better
-
Signs of anemia such as pale skin, extreme tiredness or weakness, or shortness of breath
-
Dizziness or fainting
Featured in