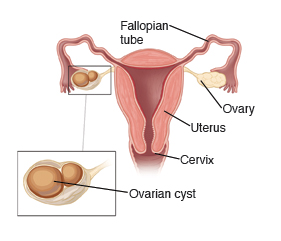
The ovaries are 2 small organs located on each side of the womb (uterus). They are part of the female reproductive system. Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluid or tissue that forms on or inside the ovaries.
Ovarian cysts are common, especially during childbearing years. There are different types of cysts. Most are harmless (benign) and go away on their own. They often cause no symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they can include mild pain or pressure in the lower belly (abdomen).
Cysts that are large can break (rupture) and bleed. This is called a hemorrhagic cyst. This may cause more severe pain and symptoms. In these cases, you may need hospital care or treatment, such as surgery. You may need more extensive treatment if a cyst causes an ovary to twist (called torsion) or if your healthcare provider suspects your cyst is cancerous. Keep in mind that most cysts are not cancerous, however.
General care
-
To help relieve pain, your healthcare provider may recommend using over-the-counter pain medicine. If needed, your provider may prescribe stronger pain medicine.
-
Using heat may help relieve your pain. Consider using a heating pad set on low or warm water bottle to relieve discomfort. Taking a warm bath may help you feel more comfortable.
-
Depending on the type of cyst you have, your healthcare provider may advise taking birth control pills. These help shrink cysts in certain cases. They may also help prevent new cysts from forming. Be sure to take these medicines as directed if they are prescribed.
-
Your healthcare provider may advise you to watch your symptoms over time to see if they go away or worsen. Regular ultrasound tests may also be advised. These can help check if a cyst goes away or grows in size.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised.
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Pain gets worse or doesn't get better with home treatment
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Weakness, dizziness, or fainting
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Featured in