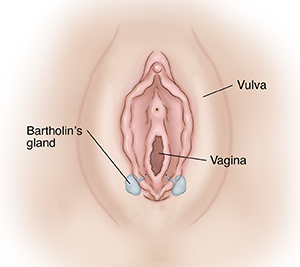
A woman has two Bartholin glands. They are located on the sides of the vaginal opening. These pea-sized glands make mucus. This mucus lubricates the outside part of the vagina (vulva). If a tube (duct) in one of these glands becomes blocked, it can cause a cyst or abscess.
What causes a Bartholin cyst or abscess?
A cyst can form when the duct of a Bartholin gland becomes blocked. The mucus can’t come out of the gland. It builds up. If the cyst becomes infected, it may turn into an abscess.
A blockage in the gland can occur from an injury or an infection, such as a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Symptoms of a Bartholin cyst or abscess
A Bartholin cyst starts as a small bump. It may cause no other symptoms. Or it may grow bigger. It can then cause swelling and pain. If an abscess forms, it can be very painful. You may have a fever. You may have trouble walking, sitting, or having sex.
Treatment for a Bartholin cyst or abscess
A cyst that doesn’t cause any symptoms may not need to be treated. It may go away on its own. But if you feel discomfort or pain, treatment options include:
-
Medicine. Over-the-counter pain medicines can help. In some cases, you may need antibiotics if an infection is severe, or a cyst or abscess comes back.
-
Sitz bath. Soaking the genital area in warm water can ease pain and sometimes help the cyst to drain on its own.
-
Drainage. Cutting open the cyst allows the fluid inside it to drain. This eases discomfort and pain. The healthcare provider may insert a tube (catheter) to help with drainage. This catheter may need to stay in place for up to 3 weeks.
-
Surgery. You may need to have the Bartholin glands removed if other treatments don’t work.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of the following occur:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Redness, swelling, or fluid leaking from the cyst that gets worse
-
Pain that gets worse
-
Symptoms that don’t get better, or get worse
-
New symptoms
Featured in
Author: Semko, Laura
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.