When you take a step or raise your hand, your joints help you move freely. But living with a worn or injured joint can make an active lifestyle painful. Your healthcare provider uses arthroscopy to see, diagnose, and often treat your joint problem. Other diagnostic tests are usually done before arthroscopy. They include a complete health history and exam. You also might get an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. After arthroscopy, you may be able to return to many of the activities you once enjoyed.
Why arthroscopy?
-
The surgeon can often find and treat the problem during one procedure.
-
The surgeon can often see the joint better than with open surgery.
-
Arthroscopy uses smaller incisions than open surgery. So you may recover faster. You may have less scarring.
How arthroscopy works
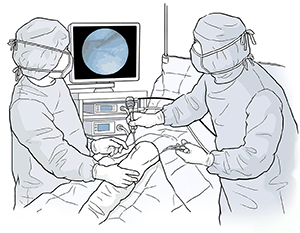
Your surgeon will use an arthroscope to look inside your joint. This is a thin instrument about the size of a pencil that contains a lens and a light source. Your healthcare provider puts the arthroscope and other special tools into the joint through tiny cuts (incisions). The arthroscope uses a camera to send an image of your joint to a monitor. This lets your surgeon see your joint more clearly. You will still get anesthesia. It will be general, spinal, or local. This means that you will not feel the arthroscopy at all.
Risks of arthroscopy
As with any surgery, arthroscopy involves some risks. These are rare but include:
-
Excess bleeding
-
Blood clots
-
Infection
-
Damage to nerves and blood vessels
-
A shift to open surgery that would need a larger incision
-
Reaction to the anesthesia