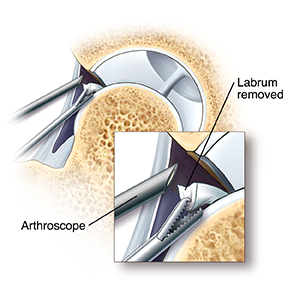
The strong, flexible ring of cartilage attached to the edge of the hip socket is called the labrum. When the labrum is torn, you may feel pain, catching, clicking, or locking in the joint. Arthroscopy is a procedure that uses special tools inserted through small incisions. With these tools, your surgeon can fix or replace a torn labrum. Your surgeon can also trim or smooth an area of the labrum that is torn.
In the operating room
Just before surgery, your healthcare providers may ask you several times which hip is to be treated. This is a standard safety measure in the operating room. You will likely receive medicine (anesthesia) to make you sleep or make the area numb, or both.
During the procedure
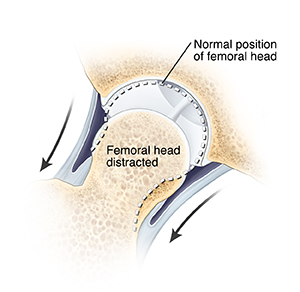
After you receive anesthesia, your leg is gently pulled to widen the hip joint. Next, your surgeon makes a few small incisions called portals. Through these portals, they insert surgical tools, including the arthroscope. The arthroscope sends images of your joint to a screen. These images allow your surgeon to look inside your joint. The joint is filled with sterile fluid to help your surgeon see more clearly.
Repairing labral tears
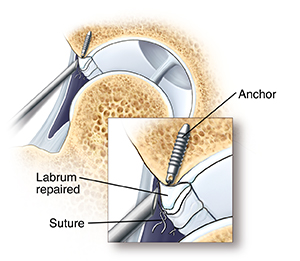
Labral tears can be removed or fixed. The torn piece of labrum may be removed by cutting, shaving, or heating the tissue (ablation). A torn labrum may be fixed by suturing (stitching) the tear to the bone. In this case, an anchor is placed in the bone and a suture ties the labrum to the anchor. Or a torn labrum can be reconstructed using a tissue graft. This can be donor tissue (allograft) or tissue from your own body (autograft). Some bone may be removed during this process using special tools. Your surgeon also uses special tools to pass the suture through tissue and tie knots through the small portals. Once your surgeon finishes, they close the portals and bandage them. Then you are taken to the recovery room.