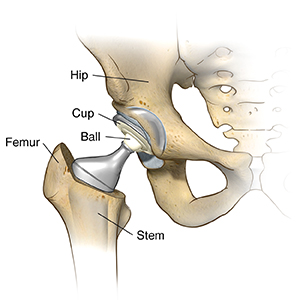
What is joint replacement surgery?
Joint replacement surgery removes and replaces an arthritic or damaged joint with an artificial joint (prosthesis). It may be considered only after other treatment choices have failed to ease pain or improve function.
Getting ready for joint replacement surgery
As with any surgery, you'll need to keep some things in mind, including:
-
Exercise. Your body tends to heal and regain function faster when it is in good physical and cardiovascular condition.
-
Medicine. Before the surgery, tell your doctor all the medicines you take. This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines. It also includes vitamins, minerals, and supplements. You may need to stop taking some medicines for a short time until after the surgery. Your primary doctor and your orthopedist will let you know if you need to do this.
-
Discharge planning. Before your surgery, talk about discharge planning with your doctor. Your discharge plan may include instructions on incision care, pain medicines, activities, special exercises, and other home care instructions.
-
Rehabilitation. People who have a total joint replacement can still lead a functional, active lifestyle. One major part of many rehab programs is exercise. This helps to restore function, mobility, and strength to the affected joint and surrounding muscles. Talk to your doctor about what your rehab program should include.
Talk with your doctor to find out any special instructions they have for you.
Possible complications linked to joint replacement surgery
Although joint replacement surgery is typically successful, complications may still occur. They include:
-
Wound infection.
-
Infection around the prosthesis.
-
Blood clots.
-
Malfunction of the prosthesis. This may be caused by wear and tear, breakage, dislocation, or loosening.
-
Nerve injury. In rare cases, nerves in the surrounding area may be damaged during the surgery.
Featured in