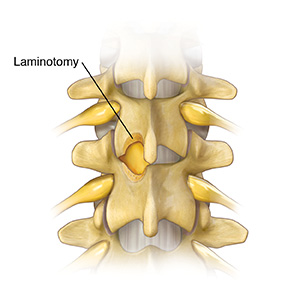
Laminotomy is a surgery that takes out a small amount of bone from the spine. This takes pressure off nerves in the low back, which eases symptoms. These surgeries are not cure-alls. But they are very good at reducing leg pain. Laminotomy can be a very useful spine procedure. Many times, there is no fusion or instrumentation needed to get good results.
Before your surgery
You will most likely need to be at the hospital on the morning of the surgery. Be sure to follow all your healthcare provider’s instructions on getting ready for surgery:
-
Follow all directions you are given for not eating or drinking before surgery.
-
If you take a daily medicine, ask if you should still take it the morning of surgery.
-
If you take any blood-thinning medicines, talk about them with your provider at least 1 week before. These include aspirin, clopidogrel, or warfarin.
-
At the hospital, your temperature, pulse, breathing, and blood pressure will be checked.
-
An IV (intravenous) line will be started. It will give you fluids and medicines as needed during surgery.
During your surgery
-
Once in the operating room, you’ll be given anesthesia.
-
After you are asleep, a cut (incision) is made near the center of your low back. Your cut may be 2 to 6 inches long. Its length depends on how many vertebrae are involved.
-
During a laminotomy, part of the lamina is taken from the vertebra above and below the pinched nerve. The lamina is bone that forms the back of the spinal canal. The small opening that is made is sometimes enough to take pressure off the nerve. But in most cases, disk matter or a bone spur that is pressing on the nerve is also taken out.
-
Once the nerve is free of pressure, the incision is closed with stitches or surgical staples.
After your surgery
After surgery, you’ll be sent to the PACU (postanesthesia care unit). When you are fully awake, you’ll be moved to your room or discharged from the hospital. The nurses will give you medicines to ease your pain. You may have a small tube (catheter) in your bladder. This tube will be removed before you go home. Soon, healthcare providers will help you get up and moving. You’ll also be shown how to keep your lungs clear.
When to call your healthcare provider
Once at home, call your healthcare provider if you have any of these:
-
Abnormal redness, heat, or fluid leaking at the incision site
-
More pain, numbness, or weakness in your leg
-
Fever of
100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher -
Swelling, warmth, or pain in your calf
-
Shortness of breath or trouble breathing