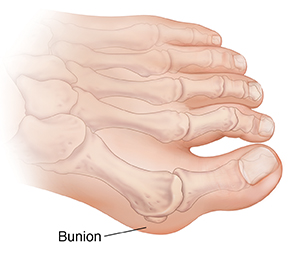
A bunion is a bony bump on the joint at the base of the big toe. A bunion changes the shape of the foot. It can also cause pain and problems using the foot.
The bony bump at the base of the big toe is caused by misalignment of the toe joint. This causes the bones to sit at an angle instead of straight. The big toe often turns in toward the second toe. In time, the big toe may start to overlap the second toe.
What causes bunions?
It's not clear what causes bunions, but many things are likely involved. Bunions often run in families. They may be more common in people who have loose joints. Wearing tight shoes may also cause bunions.
Symptoms of bunions
At first, the problem may be painless. As symptoms develop, they may include:
-
Foot pain or stiffness.
-
Swelling over the joint.
-
Redness and inflammation.
-
Skin irritation or thickened skin over the joint.
Treatment for bunions
In most cases, your health care provider will try nonsurgical treatments first. Most of these treatments won’t cure the bunion. But they can help relieve symptoms and keep the bunion from getting worse. These include:
-
Wearing low-heeled shoes with a wide toe box. This can help relieve pressure on the bunion and make walking more comfortable.
-
Using padding or special shoe inserts called orthotics. Inserts can be custom-made for your foot. They help support the foot and may change how the foot is aligned.
-
Wearing a toe splint at night. This can help hold the toe in a straighter position.
-
Putting an ice pack on a swollen joint. This can help reduce pain and swelling.
-
Doing stretching and exercises. This helps keep your joint mobile.
Your provider may advise surgery if the bunion causes severe pain or problems using the foot. During surgery, extra bone may be removed and the joint realigned.
When to get medical advice
Contact your health care provider right away if you have:
-
A fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
Chills.
-
Symptoms that don’t get better or that get worse.
-
New symptoms.