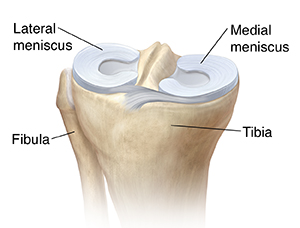
The meniscus is a tough cushion of fibrous tissue called cartilage in the knee joint. It cushions the knee. It absorbs shock and helps spread weight across the knee joint. It also works with other parts of the knee to help keep the joint stable. Injury or aging can cause the meniscus to tear and lead to pain and problems using the knee.
What causes meniscal tears?
A sudden traumatic injury can tear the meniscus. This is often because of planting the foot and twisting the knee. You might feel a "pop" when the injury happens. Sports, such as soccer, football, and basketball, are often involved. Repeated actions, such as squatting, may also lead to a tear. Breakdown of the meniscus because of aging can also lead to tears. Different types of common tears are bucket handle, flap, and radial tears.
Symptoms of meniscal tears
These can include:
-
Knee pain or "locking."
-
Knee swelling.
-
Knee stiffness.
-
Catching of the knee or inability to straighten the knee.
-
An unstable feeling in the knee.
-
Being unable to move the knee through its full range of motion.
Treatment for meniscal tears
A tear is unlikely to heal on its own. You often will need surgery to repair or remove a tear. In many cases, your health care provider will first try treatments to help relieve symptoms. These may include:
-
Resting the knee. This means staying away from any activity that puts stress on the knee joint. These include kneeling, squatting, jogging, and climbing stairs. In some cases, you may need to use crutches for a time to keep body weight off of the knee joint.
-
Cold packs. Putting a cold pack on the knee helps reduce pain and swelling.
-
A knee brace. Bracing the knee helps support it.
-
Medicine. Prescription and over-the-counter medicines can help relieve swelling and pain.
-
Exercises. Exercises help strengthen the muscles of the leg to help support the knee joint.
If these treatments don’t help relieve symptoms, or if the injury is bad, you may need surgery. This can remove or repair the meniscus to relieve symptoms and restore movement.
When to get medical care
Contact your health care provider right away if:
-
You have a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
You have chills.
-
Pain or swelling gets worse, including pain in the calf.
-
You have numbness or tingling in your leg or foot.
-
You suddenly can’t put any weight on your leg.
-
Your knee “locks.”
Author: Michels, Karen
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.