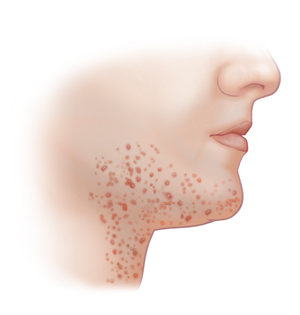
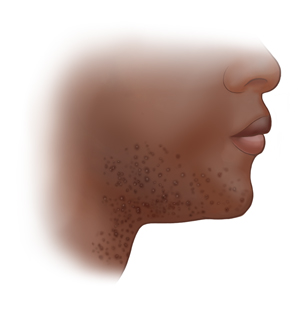
Folliculitis is a common skin condition in which the hair follicles become infected or inflamed. Follicles are the tiny holes from which hair grows out of your skin. This skin condition can occur in any place on the body where hair grows. It's often found on the neck, face, scalp, arms, legs, buttocks, chest, and back.
How to say it
foh-lihk-yoo-LI-tihs
What causes folliculitis?
An infection or irritation can cause this skin condition. Infectious folliculitis is often caused by bacteria called Staph aureus. But it may also be caused by other bacteria, viruses, or fungus. It can also be caused by a wound or irritation of the skin. Shaving is a common cause. Some cases may come from taking certain medicines, wearing tight clothing, or skin rubbing against skin.
Symptoms of folliculitis
This skin condition tends to develop quickly. It looks like little pimples on a base of a red, inflamed hair follicles. These bumps may ooze pus. They may also be:
-
Itchy.
-
Painful.
-
Red.
-
Swollen.
Treatment for folliculitis
Treatment depends on the cause of the inflammation. In some cases, this skin condition will go away on its own in a few days. But it may return. Treatment choices include:
-
A warm compress. Putting a warm, wet washcloth on the inflamed skin may help. Don't reuse the same washcloth, because that may spread infection.
-
Medicine. Many skin (topical) and oral medicines are available. Antibiotics are used for bacterial infections. Antifungal medicines are best for fungal infections. Antiviral medicines are used for viral folliculitis.
-
Good hygiene. Keeping the skin clean can help. Use a clean razor when you shave, and don't try to shave too closely. Prevent ingrown hairs after shaving. This can reduce folliculitis in the beard area. Stay away from any substances that bother your skin.
When to get medical advice
Contact your health care provider or get medical care right away if you have:
-
A fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your provider.
-
Pain that gets worse.
-
Symptoms that don’t get better or that get worse.
-
New symptoms.
Author: Semko, Laura
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.