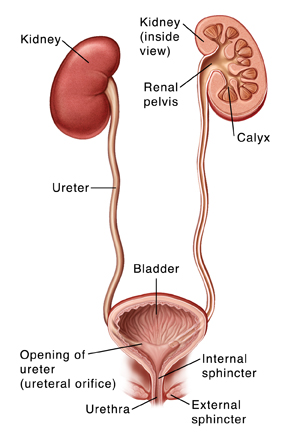
Your child’s urinary tract helps get rid of the body’s liquid waste (urine).
This system includes:
-
Kidneys. A pair of organs that filter the blood of the waste, unused minerals, and water that make up urine.
-
Calyx. Small chambers in the kidneys that drain urine into the renal pelvis.
-
Renal pelvis. Where urine collects before flowing down the ureters.
-
-
Ureters. A pair of tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
-
Bladder. An organ that stores urine until the child is ready to release it.
-
Sphincters. Ring-shaped bands of muscles. The urethral sphincters work together to hold in or release urine from the bladder. They close and tighten to hold. They open and relax to release.
-
Internal sphincter. Muscle inside the bladder that holds urine in until it’s ready to be released.
-
External sphincter. Muscle located just outside the bladder that holds urine in until it’s ready to be released. Your child has some control over when this muscle is squeezed and closed or relaxed and open.
-
-
Nerves. They signal when the bladder is filled with urine. They also tell the sphincter and bladder when it’s time to empty the bladder.
-
Urethra. Tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Featured in