An allergic reaction is a set of symptoms caused by an allergen. An allergen is something that causes your immune system to react abnormally. It releases various chemicals. These include histamine. Histamine causes swelling and itching. An allergic reaction may affect the entire body. This is called a general allergic reaction. Often, symptoms affect only 1 part of the body. This is called a local allergic reaction.
You are having an allergic reaction. Almost anything can cause it. Different people are allergic to different things. It's usually something that you ate or swallowed, came into contact with by getting or putting it on your skin or clothes, or something you breathed in the air. This can be very annoying and sometimes scary.
Most people think of allergic reactions when they have a rash or itchy skin. Other symptoms can include:
-
Itching of the eyes, nose, and roof of the mouth
-
Runny or stuffy nose
-
Watery eyes
-
Sneezing or coughing
-
A blocked feeling in the ear
-
Red, raised, itchy rash called hives
-
Red and purple spots
-
Rash, redness, welts, blisters
-
Itching, burning, stinging, pain
-
Dry, flaky, cracking, scaly skin
Severe symptoms include:
-
Swelling of the face, lips, mouth, throat, or other parts of the body
-
Hoarse voice
-
Trouble swallowing, feeling like your throat is closing
-
Trouble breathing, wheezing
-
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps
-
Feeling faint or lightheaded, rapid heart rate
Sometimes the cause of an allergic reaction may be obvious. But there are so many things that can cause a reaction that you may not be able to figure it out. The most important things to help find your allergen are to remember:
-
Where you were, such as in a forest, factory, grocery store, or paint store
-
When it started
-
What you were doing at the time or just before that
-
What activities you were involved in
-
If you were exposed to anything new
Below are some common causes of allergies. Some of these can cause severe general allergic reactions. Others can cause mild to moderate symptoms. But remember that almost anything can cause a reaction. You may not even be aware that you came into contact with one of these things:
-
Dust, mold, pollen
-
Plants (common ones are poison ivy and poison oak, but there are many others)
-
Animals
-
Foods, such as shrimp, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, milk products, wheat, and eggs
-
Food colorings, flavorings, and additives
-
Insect bites or stings, such as bees, mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks
-
Medicines, such as penicillin, sulfa medicines, aspirin, and ibuprofen. But any medicine can cause a reaction.
-
Jewelry, such as nickel or gold. This can be new, or something you’ve worn for a while, including zippers and buttons.
-
Latex, such as in gloves, clothes, toys, balloons, or some tapes. Some people allergic to latex may also have problems with foods like bananas, avocados, kiwi, papaya, or chestnuts.
-
Lotions, perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, shampoos, skincare products, nail products
-
Chemicals or dyes in clothing, linen, cleaners, hair dyes, soaps, iodine
Many viruses and common colds can cause a rash (such as hives) that is not an allergic reaction. Sometimes it's hard to tell the difference between allergies, sensitivity, or an intolerance to something. This is especially true with food. Many things can cause diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and skin irritation.
Home care
The goal of treatment is to help relieve the symptoms and get you feeling better. The rash will usually fade over several days. But it can sometimes last a couple of weeks. Over the next couple of days, there may be times when it gets a little worse, and then better again. Here are some things to do:
-
If you know what you are allergic to, stay away from it. Future exposures may cause similar or sometimes worse symptoms.
-
Don't wear tight clothing and stay away from anything that heats up your skin, such as hot showers or baths, and direct sunlight. Heat will make itching worse.
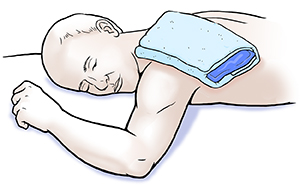
-
An ice pack will relieve local areas of intense itching and redness. To make an ice pack, put ice cubes in a plastic bag that seals at the top. Wrap it in a thin, clean towel. Apply the ice pack for 5 to 10 minutes. Don’t put the ice directly on the skin because it can damage the skin.
-
Oral diphenhydramine is an over-the-counter antihistamine sold at pharmacies and grocery stores. Unless a prescription antihistamine was given, diphenhydramine may be used to reduce itching if large areas of the skin are involved. It may make you sleepy. So be careful using it in the daytime or when going to school, working, or driving. Note: Don’t use diphenhydramine if you have glaucoma or if you have trouble urinating because of an enlarged prostate. There are other antihistamines that won’t make you so sleepy. These are good choices for daytime use. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for suggestions.
-
Don’t use diphenhydramine cream on your skin unless prescribed. It may cause a worse reaction in some people.
-
To help prevent an infection, don't scratch the affected area. Scratching may make the reaction worse and damage your skin. It can also lead to an infection. Always check the affected areas for signs of an infection.
-
Call your healthcare provider and ask what you can use to help decrease the itching.
-
To decrease your exposure to allergens, try the following:
-
Use heat-steam to clean your home.
-
Use high-efficiency particulate (HEPA) vacuums and filters.
-
Stay away from food and pet triggers.
-
Kill any cockroaches and use pest control to keep infestations from happening again.
-
Clean your house often.
-
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised. You may be referred to an allergist. If you had a severe reaction today, or if you have had several mild to medium allergic reactions in the past, ask your provider about allergy testing. This can help you find out what you are allergic to. If you had a severe reaction that included dizziness, fainting, or trouble breathing or swallowing, ask your provider about carrying epinephrine and wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace. You can also ask if allergy immunotherapy (such as allergy shots) may be right for you.
Call 911
Call
-
Trouble breathing or swallowing, wheezing
-
Cool, moist, pale skin
-
Shortness of breath
-
Hoarse voice or trouble speaking
-
Confusion
-
Very drowsy or trouble awakening
-
Fainting or loss of consciousness
-
Rapid heart rate
-
Feeling of dizziness or weakness or a sudden drop in blood pressure
-
Feeling of doom
-
Feeling lightheaded
-
Severe nausea or vomiting, or diarrhea
-
Seizure
-
Swelling in the face, eyelids, lips, mouth, throat, or tongue
-
Drooling
When to seek medical advice
Call your healthcare provider or get medical care right away if any of these occur:
-
Spreading areas of itching, redness, or swelling
-
Nausea or stomach cramps or abdominal pain
-
Symptoms that continue, get worse, or happen more than once
-
Spreading areas of redness, swelling, or itching
-
Signs of infection at the affected site:
-
Spreading redness
-
Increased pain or swelling
-
Fluid or colored drainage from the site
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-