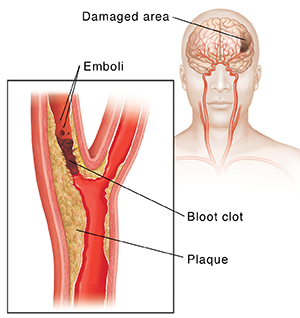
The carotid arteries are large blood vessels that carry blood to the brain. When these arteries are healthy, the brain gets all the oxygen and nutrients it needs to function well. But if the carotid arteries are damaged, this can greatly increase your risk of a stroke. A stroke is a sudden loss of brain function caused by a lack of blood flow and oxygen.
How artery damage can lead to a stroke
A healthy carotid artery is smooth on the inside, like a tube. But health problems such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking can damage the inside of the artery wall and make it rough. This lets fatty deposits, called plaque, build up on the artery wall. Blood clots called emboli may also form on the plaque. If pieces of plaque or emboli break off, they can flow in the blood and get stuck in a small blood vessel in the brain. This blocks the blood flow to a part of the brain, and causes a stroke.
Symptoms of a stroke
Below are common symptoms of a stroke. Call 911 right away if you have any of these symptoms. Fast medical treatment for a stroke is vital. The longer you wait to get help, the more damage a stroke can do.
-
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
-
Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding other people
-
Sudden trouble seeing in 1 or both eyes
-
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination
-
Sudden, severe headache with no known cause
-
Sudden new seizures
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a mini-stroke. It’s a warning sign that a larger stroke may happen in the near future. A TIA is when an artery to the brain is blocked for a brief time. This will cause symptoms just like those that happen with a stroke. But with a TIA, they last a short period of time, from a few seconds to a few hours. Never ignore any TIA or stroke symptoms. Call 911 right away.
B.E. F.A.S.T.
B.E. F.A.S.T. is an easy way to remember the signs of a stroke or TIA. When you see these signs, call
B.E. F.A.S.T. stands for:
-
B is for balance. Sudden loss of balance or coordination.
-
E is for eyes. Vision changes in one or both eyes.
-
F is for face drooping. One side of the face is drooping or numb. When the person smiles, the smile is uneven.
-
A is for arm weakness. One arm is weak or numb. When the person lifts both arms at the same time, one arm may drift downward.
-
S is for speech difficulty. You may notice slurred speech or trouble speaking. The person can't repeat a simple sentence correctly when asked.
-
T is for time to call 911. If someone shows any of these symptoms, even if the symptoms go away, call
911 right away. Make note of the time the symptoms first appeared.