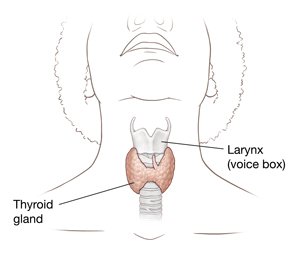
The thyroid is a gland in the neck, just below the voicebox. It is an endocrine gland. Endocrine glands make hormones. These are chemicals that carry messages through the bloodstream to other parts of the body. The thyroid gland makes thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland is managed by the pituitary gland, which sits at the base of the brain.
Keeping the body working right
Thyroid hormones help keep all the cells in the body working right. It does this by controlling the metabolism. This is the rate at which every part of the body functions. The right amount of thyroid hormones keep the metabolism at a healthy pace. This helps the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs work well. A balanced metabolism also helps ensure a healthy temperature, heart rate, energy level, and growth rate. Thyroid hormones also play a vital role in children's growth.
The thyroid-pituitary cycle
The thyroid hormone needs to be kept at a healthy level. A complex cycle maintains this level. The cycle starts with the pituitary gland. This gland checks the thyroid hormone level in the blood.
Depending on the level, the pituitary sends thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) through the blood to the thyroid gland. TSH tells the thyroid gland how much thyroid hormone to make. In response to TSH, the thyroid makes thyroid hormone. Then thyroid hormone is sent into the blood to the rest of the body. The pituitary senses the hormone level, adjusts the TSH level, and the cycle continues.