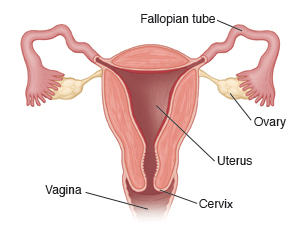
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs. These include the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
PID is a common problem. It's most often caused by gonorrhea or chlamydia. These are bacterial infections that are spread through sex. For this reason, they are known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). PID can also be caused by other infections, though this is much less common.
When PID is found and treated early, it can often be cured. If not treated promptly, PID can lead to serious health problems. These include chronic pelvic pain and damage to the reproductive organs. PID can also lead to infertility. And it can increase the risk of tubal pregnancy. Mild cases of PID can often be treated at home. Severe cases of PID may need to be treated in the hospital.
Home care
-
You will likely be prescribed a combination of antibiotics. Be sure to take the medicines exactly as directed.
-
To help relieve pain, you may take over-the-counter pain medicine. Pain medicine may also be prescribed, if needed.
-
Tell any partners you’ve had sex with about your condition. They will need to be tested for infection and treated as well.
-
Don't have sex until you and any partners have finished treatment and tests show that you are no longer infected.
Prevention
-
If you choose to have sex, make sure to practice safer sex. For instance, have sex with only one partner who only has sex with you. Ask your partner to be tested for STIs. Each time you have sex, use latex condoms. These help reduce the risk for STIs.
-
Don't douche unless advised to by your healthcare provider. Douching may increase the risk for PID.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider, or as advised.
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of the following occur:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Symptoms don't improve after 2 days of treatment
-
New or increasing pain in your lower belly or back
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
-
Abnormal vaginal discharge
-
Weakness, dizziness or fainting
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Trouble with urination or pain and burning during urination
-
Rash or joint pain
-
Painful open sores around the vagina
-
Swollen or painful lymph nodes in the groin (these may be felt as lumps in the groin)
To learn more
To learn more about PID and STIs, contact:
-
CDC National STI Hotline at www.cdc.gov/std/ or 800-232-4636
Featured in