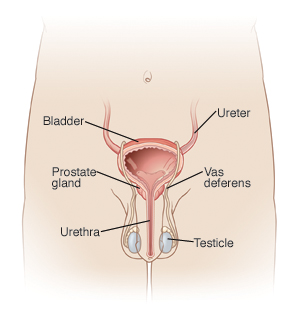
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system. It is located at the base of your bladder and in front of your rectum. It surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine. The prostate makes the fluid that carries sperm. Prostatitis can happen with or without infection. Most cases of prostatitis are long term (chronic). Most do not include a bacterial infection. There are 4 types of prostatitis:
-
Chronic prostatitis. Also called chronic pelvic pain syndrome. It is often an inflammatory condition, not an infection. It's not clear what causes it. Certain triggers like injury, nerve damage, chemicals in the urine, or your body's immune response to UTI may play a role. The symptoms include:
-
Pain in the rectum, urethra, bladder, or scrotum that lasts more than 3 months.
-
Inability to completely empty the bladder.
-
Urinary urgency, feeling the need to empty the bladder.
-
Urinary frequency, feeling the need to pee often.
-
Burning with urination.
-
-
Chronic bacterial prostatitis. This is less common but mostly seen in older men. It is a mild bacterial infection that lasts for several months. The symptoms may be similar to acute bacterial prostatitis. But they are less severe and often develop slowly, sometimes over years.
-
Acute bacterial prostatitis happens suddenly. This often occurs in men younger than 35. It is from a bacterial infection. You may have severe symptoms, such as:
-
Fever.
-
Chills.
-
Muscle aches.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Pain in the area between the scrotum and anus (perineum).
-
Pain or a burning feeling when peeing.
-
Pain when ejaculating.
-
Having a hard time peeing.
-
Blood or pus in the urine.
-
Blood in the semen.
-
-
Asymptomatic prostatitis.. This type does not have any symptoms. It is usually discovered while doing tests for other problems.
Who is at risk?
Prostatitis is the most common urinary tract problem for men younger than age 50. It's the third most common urinary tract problem for men older than age 50. Other factors include:
-
Using an indwelling urinary catheter.
-
Pelvic trauma.
-
Urinary tract infection.
-
Enlarged prostate.
-
Trauma.
-
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including gonorrhea and chlamydia.
How is it diagnosed?
Your health care provider may use tests to diagnose your condition:
-
Digital rectal exam. During this your provider will insert a gloved finger into the rectum to check the prostate for swelling or tenderness, a prostate massage may also be performed. The prostate causes the release of seminal fluid built up in the gland, which your health care provider may want to test for bacteria.
-
Culture test on prostate fluids or discharge from the penis. urine, and blood analysis. This will help figure out if bacteria are the cause. A culture test can help your provider know if you're taking the correct antibiotic.
-
Urodynamic tests. These are done to see how well the bladder and urethra store and release urine.
-
Transrectal ultrasound. The technician inserts a transducer slightly larger than a pen into the man’s rectum next to the prostate. The ultrasound image shows the size of the prostate and any abnormalities, such as tumors. Transrectal ultrasound cannot reliably diagnose prostate cancer.
-
Cystoscopy. A small tube is inserted into your urethra to look at your bladder and prostate gland.
-
Other imaging studies like CT scan and MRI are done if the rectal exam is not normal. It can help rule out tumors.
How is it treated?
Treatment can include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medicine, prostate medicines, and stool softeners. Alpha-adrenergic blockers help relax the muscles of the prostate gland.
Home care
These guidelines will help you care for yourself at home:
-
Rest at home until the fever is gone and you are feeling better.
-
A warm sitz bath may offer some relief. Fill a tub with 6 inches of warm water. Allow the water to run so you can keep it warm for 10 to 15 minutes.
-
Drink plenty of fluids. Don't drink alcohol or caffeine until all symptoms are gone.
-
If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
-
Stay away from things that irritate your bladder, such as alcohol, caffeinated foods and drinks, citrus juices, and spicy foods.
-
Constipation causes straining and pain. Prevent constipation by eating natural laxatives, such as prunes, fresh fruits, and whole-grain cereals. If needed, use a mild over-the-counter (OTC) laxative for constipation. An OTC stool softener may be used to keep the stools soft.
-
If sex is uncomfortable or painful, don't have sex until symptoms get better.
-
You may use OTC medicines for pain and fever, unless another medicine was given. If you have chronic liver or kidney disease, talk with your provider before using these medicines. Also talk with your provider if you've ever had a stomach ulcer or digestive tract bleeding, or if you take any other medicines.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your provider, a urologist, or as advised to be sure you are responding to treatment. Your provider may want to see you after you finish your antibiotics to be sure the infection has cleared. If a culture was taken, you may call for the results as directed.
Call 911
Call 911 if:
-
You have weakness, dizziness, or fainting.
When to contact your doctor
Contact your provider right away if:
-
You have a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as advised by your provider.
-
You are unable to pee for 8 hours.
-
The pressure or pain in your bladder gets worse.
-
You have painful swelling of the testicle or scrotum.
Featured in